Using renewable energy is one of the easiest and most affordable ways for a business to cut its carbon footprint and reach larger sustainability goals like net zero. As renewable technologies have improved and tariffs have become cheaper, more SMEs have joined larger firms in supporting the fight against climate change. For businesses that want to do their bit, but aren’t sure where to start, choosing renewables is a purposeful step on the pathway to sustainability.
The way we generate energy is changing
In the first half of the 21st century, the energy system will undergo a major shift away from fossil fuels.
Traditionally, we have created electricity by burning fossil fuels like coal and natural gas to generate energy. These fuels are not replenished quickly enough to be sustainable. At current rates, it is estimated that the world’s supply of fossil fuels will be used up by 2060.
The main problem with fossil fuels is that they damage the planet and human health. Fossil fuels release carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases when they’re burned. These greenhouse gases trap heat in the atmosphere, contributing to global warming and climate change.
Most of the UK’s air pollution is also caused by fossil fuels, which release a number of harmful gases and chemicals when they’re burned. Coal is the most carbon-intensive fossil fuel that we can burn and is the biggest single source of global temperature increases in the post-industrial era.
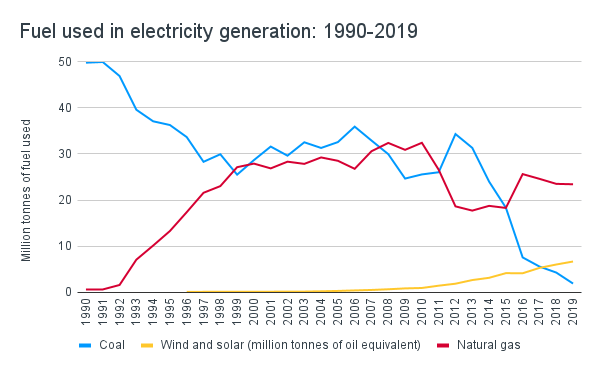
In recent decades, the amount of coal used in UK power stations has dropped significantly and is now approaching zero. Natural gas, which is still damaging but produces fewer harmful emissions than coal, has picked up some of the slack. The most positive recent change, however, is the rapid expansion of renewable energy sources like wind and solar.
Source: Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy. Historical Electricity Data: 1920 to 2019.
What is renewable energy?
Renewable energy is energy that’s created from sustainable sources.
While fossil fuels are all finite resources, renewable power generators use natural resources like wind, solar and tidal energy to produce energy. Green gases like biogas - which can be produced from organic waste - can also be used to produce low carbon heat.
Compared to fossil fuels, the key advantage of renewable energy is that it has a much lower impact on the environment and on human health. There is, however, an important distinction between being renewable and zero carbon.
Wind and solar power can be created without producing any greenhouse gases. But renewable fuels like biomass and biogas do emit harmful gases when they’re burned. These fuels are still thought to be cleaner than fossil fuels, because they are made using carbon dioxide-absorbing organic matter.
Nuclear power is an example of a technology that is zero carbon but not renewable, because nuclear fuel is not sustainable.
Get help to act on climate change
When shaping your energy approach, you can make the most of your investment by aligning business energy with your broader business objectives. For this, you need a partner with knowledge of the changing energy supply landscape, a strong service record and flexible energy supply options – with a focus on renewables. That’s British Gas. With our British Gas experts we are uniquely positioned to provide an end to- end service, making business supply an integral part of your overall solution. Whether you’re looking for transition to renewables or just a better deal, we can shape an integrated energy solution that balances cost and environmental impact.